Category Archives: IT
iptable nf_inet_hooks
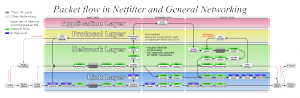
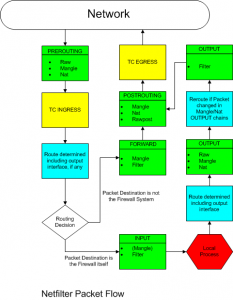
Netfilter places
从上网络包发送接受流程图中看出,可以在不同的地方注册Nefilter的hook函数.由如下定义:
enum nf_inet_hooks {
NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING, //0
NF_INET_LOCAL_IN,
NF_INET_FORWARD,
NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT,
NF_INET_POST_ROUTING, //4
NF_INET_NUMHOOKS
};
NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING: incoming packets pass this hook in the ip_rcv() (linux/net/ipv4/ip_input.c) function before they are processed by the routing code.
NF_INET_LOCAL_IN: all incoming packets addressed to the local computer pass this hook in the function ip_local_deliver().
NF_INET_FORWARD: incoming packets are passed this hook in the function ip_forwared().
NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT: all outgoing packets created in the local computer pass this hook in the function ip_build_and_send_pkt().
NF_INET_POST_ROUTING: this hook in the ipfinishoutput() function before they leave the computer.
how-to-filter-network-packets
C++ std map
Declare
std::map
Add
first[‘a’]=10;
first[‘b’]=30;
first[‘c’]=50;
first[‘d’]=70;
Test key exist:
if ( first.find(“f”) == first.end() ) {
// not found
} else {
// found
}
it = mymap.begin();
while (it != mymap.end()) {
if (something)
mymap.erase(it++);
else
it++;
}
C++ 11
std::map<K, V>::iterator itr = myMap.begin();
while (itr != myMap.end()) {
if (ShouldDelete(*itr)) {
itr = myMap.erase(itr);
} else {
++itr;
}
}
Compare Two Java byte Arrays Example
/*
Compare Two Java byte Arrays Example
This java example shows how to compare two byte arrays for equality using
Arrays.equals method.
*/
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CompareByteArraysExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//create byte arrays
byte[] byteArray1 = new byte[]{7,25,12};
byte[] byteArray2 = new byte[]{7,25,12};
/*
To compare two byte arrays use,
static boolean equals(byte array1[], byte array2[]) method of Arrays class.
It returns true if both arrays are equal. Arrays are considered as equal
if they contain same elements in same order.
*/
boolean blnResult = Arrays.equals(byteArray1,byteArray2);
System.out.println(“Are two byte arrays equal ? : ” + blnResult);
/*
Please note that two byte array references pointing to null are
considered as equal.
*/
}
}
/*
Output of the program would be
Are two byte arrays equal ? : true
*/
C++ Get current hour, minutes of the day
#include <time.h>
time_t theTime = time(NULL);
struct tm *aTime = localtime(&theTime);
int day = aTime->tm_mday;
int month = aTime->tm_mon + 1; // Month is 0 – 11, add 1 to get a jan-dec 1-12 concept
int year = aTime->tm_year + 1900; // Year is # years since 1900
int hour=aTime->tm_hour;
int min=aTime->tm_min;
c++ code std::map iterator map
map<DWORD,MACADDR> arpmap=CAddressHelper::GetARPCache();
map<DWORD,MACADDR>::iterator it;
for (it = arpmap.begin(); it != arpmap.end(); ++it) {
MACADDR &sMac = (*it).second;
const DWORD &nIP=(*it).first;
}
c++ 11
for (auto x: arpmap) {
cout << x.first << endl;
}
C++ Code Convert Hex string back to Char buffer
int _helpper_Hex2Char(unsigned char & p_cChar,unsigned char p_Value,int & p_nOdd)
{
p_cChar&=0xf0;
p_Value&=0x0f;
p_cChar|=p_Value;
if(p_nOdd++%2) p_cChar<<=4; //first part
return p_nOdd%2?1:0; //if it is odd, then index need to +1 , other wise, index +0;
}
string _helper_Hex2Buffer(string p_sHexStr)
{
string sReturn = "";
unsigned char *buf=new unsigned char[p_sHexStr.length()];
memset(buf,0,p_sHexStr.length());
int nIndex=0;
int nOdd=1;
for (int i = 0; i < p_sHexStr.length (); ++i)
{
switch (p_sHexStr [i])
{
case '0':
{
nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x00,nOdd);
break;
}
case '1':
{
nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x01,nOdd);
break;
}
case '2': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x02,nOdd); break;
case '3': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x03,nOdd); break;
case '4': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x04,nOdd); break;
case '5': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x05,nOdd); break;
case '6': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x06,nOdd); break;
case '7': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x07,nOdd); break;
case '8': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x08,nOdd); break;
case '9': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x09,nOdd); break;
case 'a': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x0a,nOdd); break;
case 'b': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x0b,nOdd); break;
case 'c': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x0c,nOdd); break;
case 'd': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x0d,nOdd); break;
case 'e': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x0e,nOdd); break;
case 'f': nIndex+=_helpper_Hex2Char(buf[nIndex],0x0f,nOdd); break;
default:
continue;
}
}
sReturn.append((char *)buf,nIndex);
delete buf;
return sReturn;
}
NDK Enable PIE manually
# Enable PIE manually. Will get reset on $(CLEAR_VARS). This
# is what enabling PIE translates to behind the scenes.
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -fPIE
LOCAL_LDFLAGS += -fPIE -pie
std::list example:: iterate list
Two ways to iterate list
1. use this one when need to remove item from the list.
std::list<int>::iterator it = m_clientList.begin();
while (it != m_clientList.end()) {
if (xxxx) {
it = m_clientList.erase(it);
} else {
++it;
}
}
2. normal iterate
list<int> copylist = GetClients();
for (std::list<int>::iterator it = copylist.begin();
it != copylist.end(); ++it) {
int n = *it;
//do something with n
}