LTE
Bell/Telus : LTE AWS (1700 MHz) or LTE 700 MHz bands, or UMTS/HSPA compatible on 850/1900 MHz bands.
Device:
Ipad mini Cell:
- UMTS/HSPA/HSPA+/DC-HSDPA (850, 900, 1700/2100, 1900, 2100 MHz); GSM/EDGE (850, 900, 1800, 1900 MHz)
- CDMA EV-DO Rev. A and Rev. B (800, 1900 MHz)
- LTE (Bands 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 13, 17, 18, 19, 20, 25, 26)3
Sumsung:
-
Network compatibilityLTE
-
Maximum download speedUp to 75 Mbps
-
LTE compatibilityYes
-
HSPA/UMTS compatibility850/1900/2100 MHz
-
GPRS/EDGE compatibility850/900/1800/1900 MHz
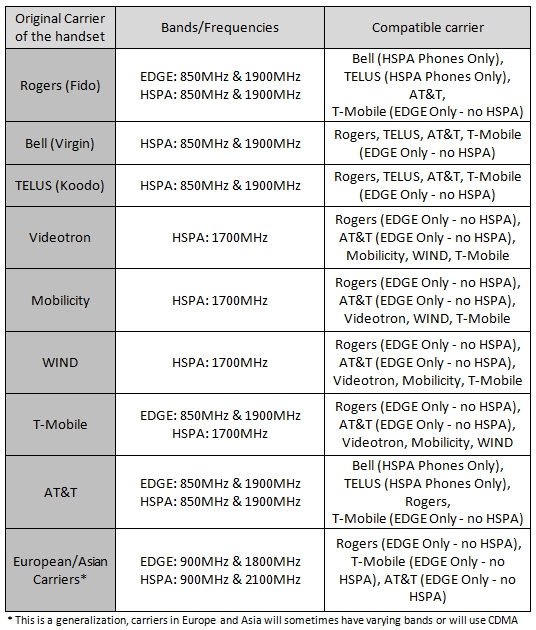
1. Telus (Koodo)
2G
CDMA 850/1900
EVDO 850/1900
3G (and fake 4G)
HSDPA 850/1900
HSPA+ 850/1900
UMTS 850/1900
WCDMA 850/1900
1x EV-DO CDMA2000
4G (called 4G+)
LTE 1700/2100
——————————————————————–
2. Bell (Virgin Mobile, PC Mobility)
2G
CDMA 850/1900
EVDO 850/1900
3G (and fake 4G)
HSDPA 850/1900
HSPA+ 850/1900
UMTS 850/1900
WCDMA 850/1900
1x EV-DO CDMA2000
4G
LTE 1700
—————————————————————————
3. Rogers (Fido, Petro-Canada Mobility)
2G
GSM 850/1900
GPRS 850/1900
EDGE 850/1900
3G (and fake 4G)
HSDPA 850/1900
HSPA+ 850/1900
UMTS 850/1900
WCDMA 850/1900
4G
LTE 1700